Analysis suggests child bullies have higher risk for substance use later in life
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Children and adolescents who bully their peers have a higher risk for drug, alcohol and tobacco use later in life, according to the results of a meta-analysis published in Pediatrics. Charlotte Vrijen, PhD, a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Groningen in the Netherlands, and colleagues reviewed existing evidence regarding the association between peer bullying perpetration in

The 4 Traits That Put Kids at Risk for Addiction - The New York Times

Behind the numbers: ending school violence and bullying
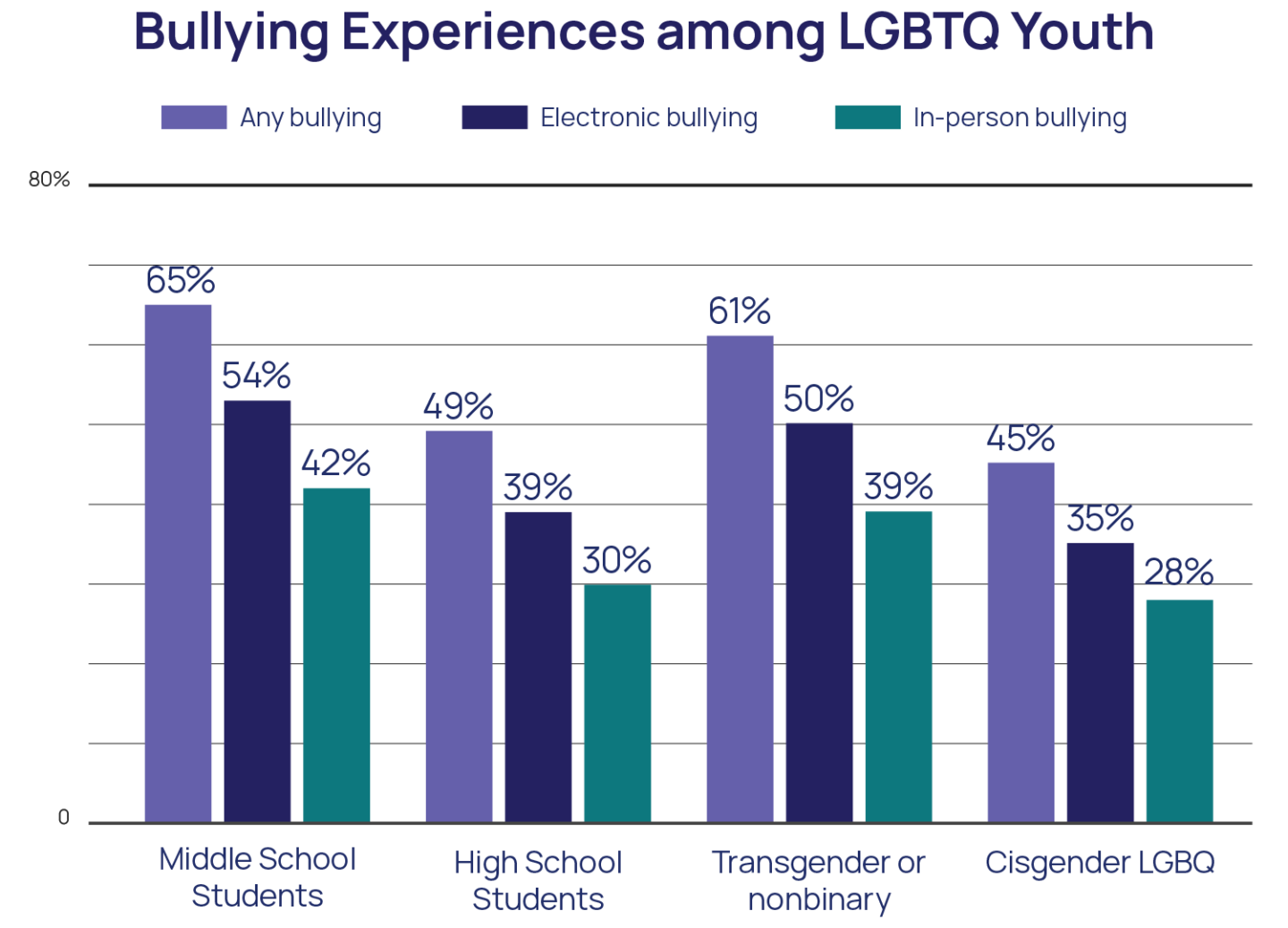
Bullying and Suicide Risk among LGBTQ Youth
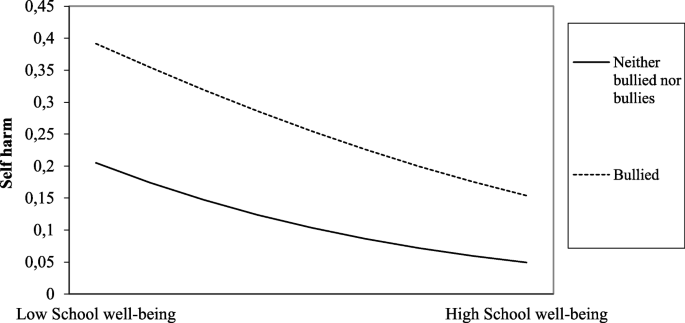
The relationship between self-harm and bullying behaviour: results from a population based study of adolescents, BMC Public Health

The causes and effects of bullying in schools and how to help

School bullying - Wikipedia

Impact of Bullying in Childhood on Adult Health, Wealth, Crime, and Social Outcomes - Dieter Wolke, William E. Copeland, Adrian Angold, E. Jane Costello, 2013

Childhood Risk and Protective Factors as Predictors of Adolescent Bullying Roles

Bullied Kids More Likely to Commit Crimes As Adults

Health advisory on social media use in adolescence
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






