Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features and variants in both the CREBBP and EP300 genes: a case report, BMC Medical Genetics
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
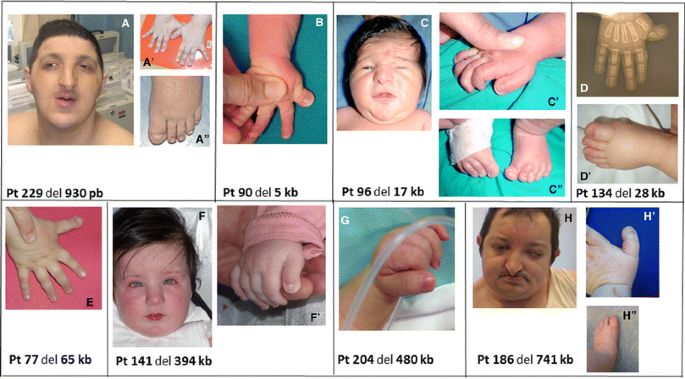
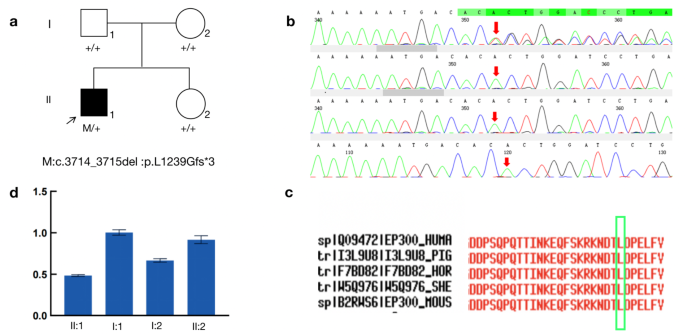
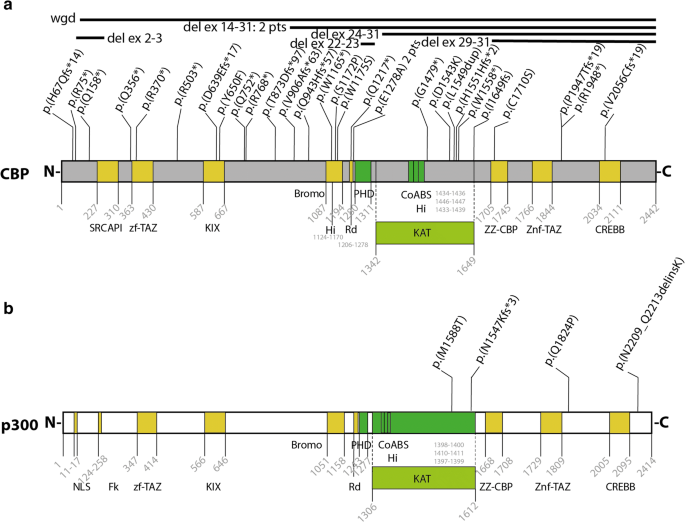
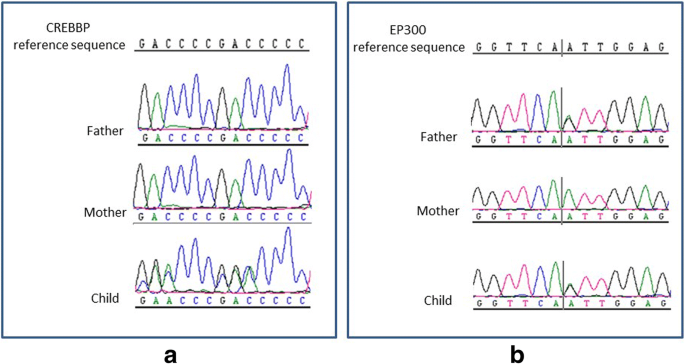
Background Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) Type 1 (OMIM 180849) is characterized by three main features: intellectual disability; broad and frequently angulated thumbs and halluces; and characteristic facial dysmorphism. Case presentation We report on a Saudi boy with RSTS Type 1 and the following distinct features: a midline notch of the upper lip, a bifid tip of the tongue, a midline groove of the lower lip, plump fingers with broad / flat fingertips, and brachydactyly. The child was found to be heterozygous in the CREBBP gene for a sequence variant designated c.4963del, which is predicted to result in premature protein termination p.Leu1655Cysfs*89. The child and his father were also found to be heterozygous in the EP300 gene for a sequence variant designated c.586A > G, which is predicted to result in the amino-acid substitution p.Ile196Val. Conclusion Our report expands the clinical spectrum of RSTS to include several distinct facial and limb features. The variant of the CREBBP gene is known to be causative of RSTS Type 1. The variant in the EP300 gene is benign since the father carried the same variant and exhibited no abnormalities. However, functional studies are required to investigate if this benign EP300 variant influences the phenotype in the presence of disease-causing CREBBP gene mutations.

Further delineation of an entity caused by CREBBP and EP300 mutations but not resembling Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Menke - 2018 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library

PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome medical guidelines
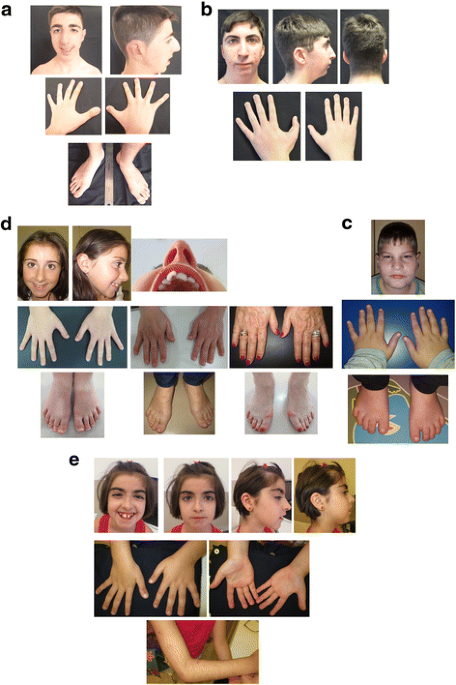
Frontiers Genetic Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome With Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) and Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES): Case Series With a Novel CREBBP Variant
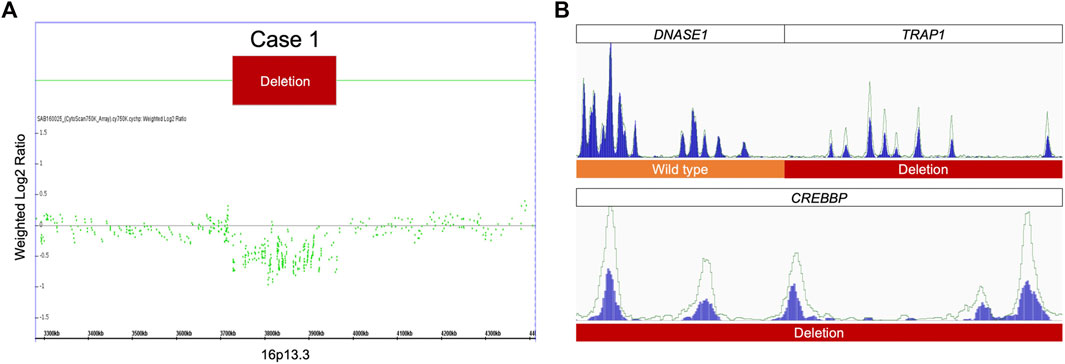
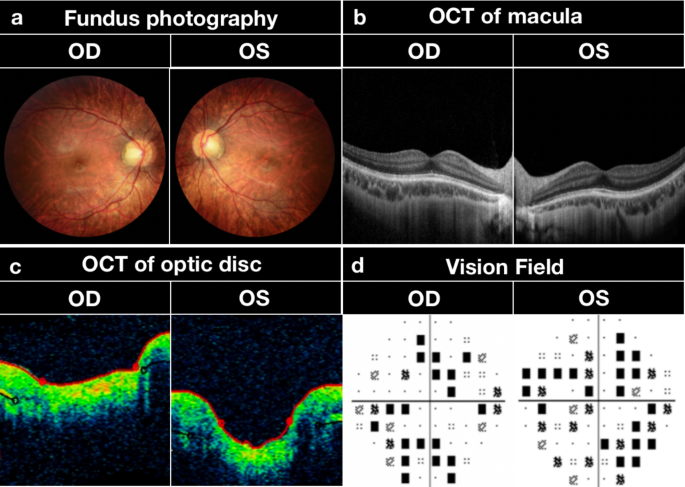
De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia, BMC Medical Genomics
Prevalence of Immunological Defects in a Cohort of 97 Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome Patients

EP300‐related Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: Highlighted rare phenotypic findings and a genotype–phenotype meta‐analysis of 74 patients - Cohen - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library
De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia, BMC Medical Genomics
Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome in a Saudi boy with distinct features and variants in both the CREBBP and EP300 genes: a case report, BMC Medical Genetics

Further delineation of an entity caused by CREBBP and EP300 mutations but not resembling Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Menke - 2018 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)