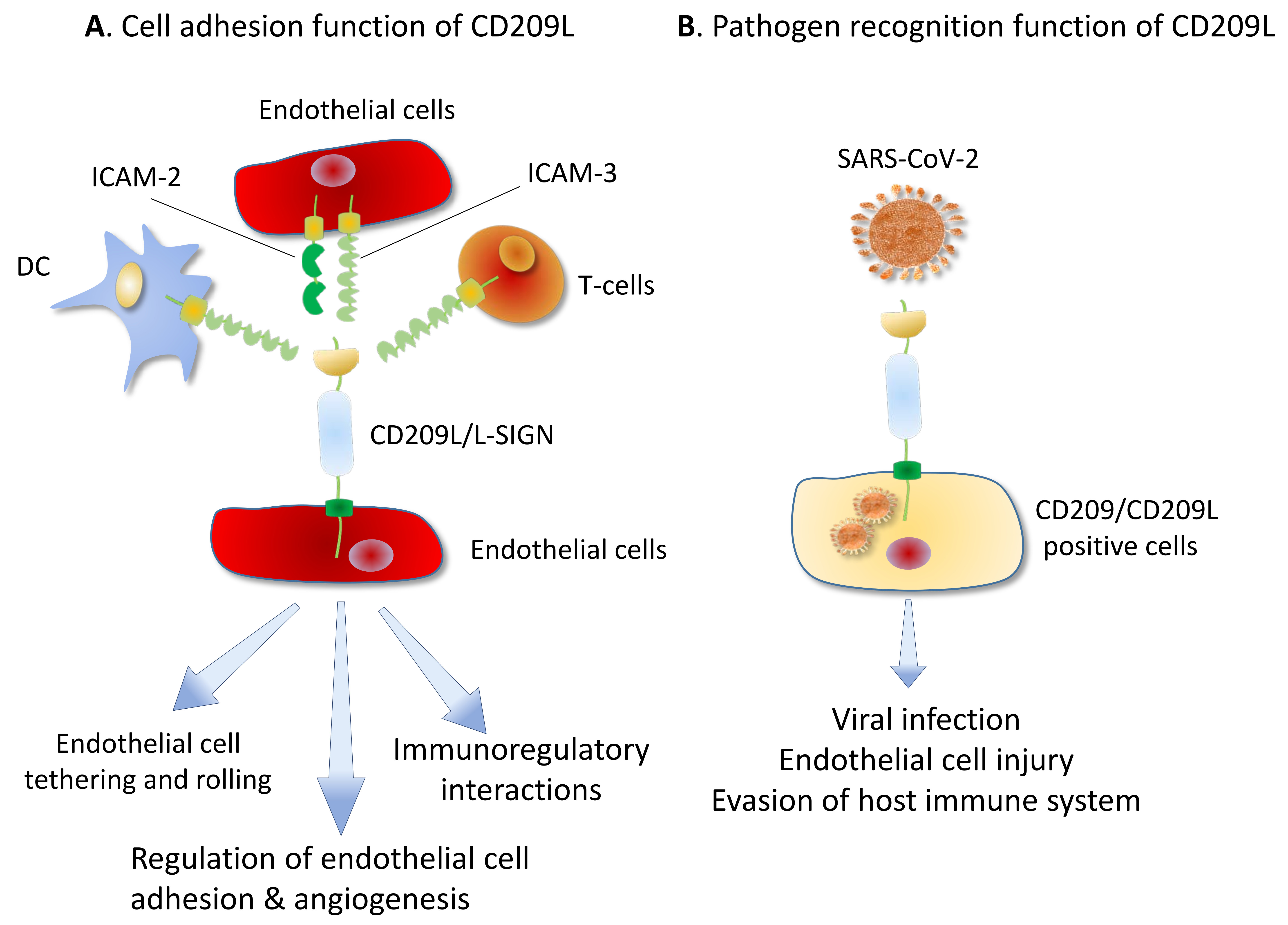
CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN Act as Receptors for SARS-CoV-2
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Epigenetic glycosylation of SARS-CoV-2 impact viral infection through DC&L-SIGN receptors - ScienceDirect
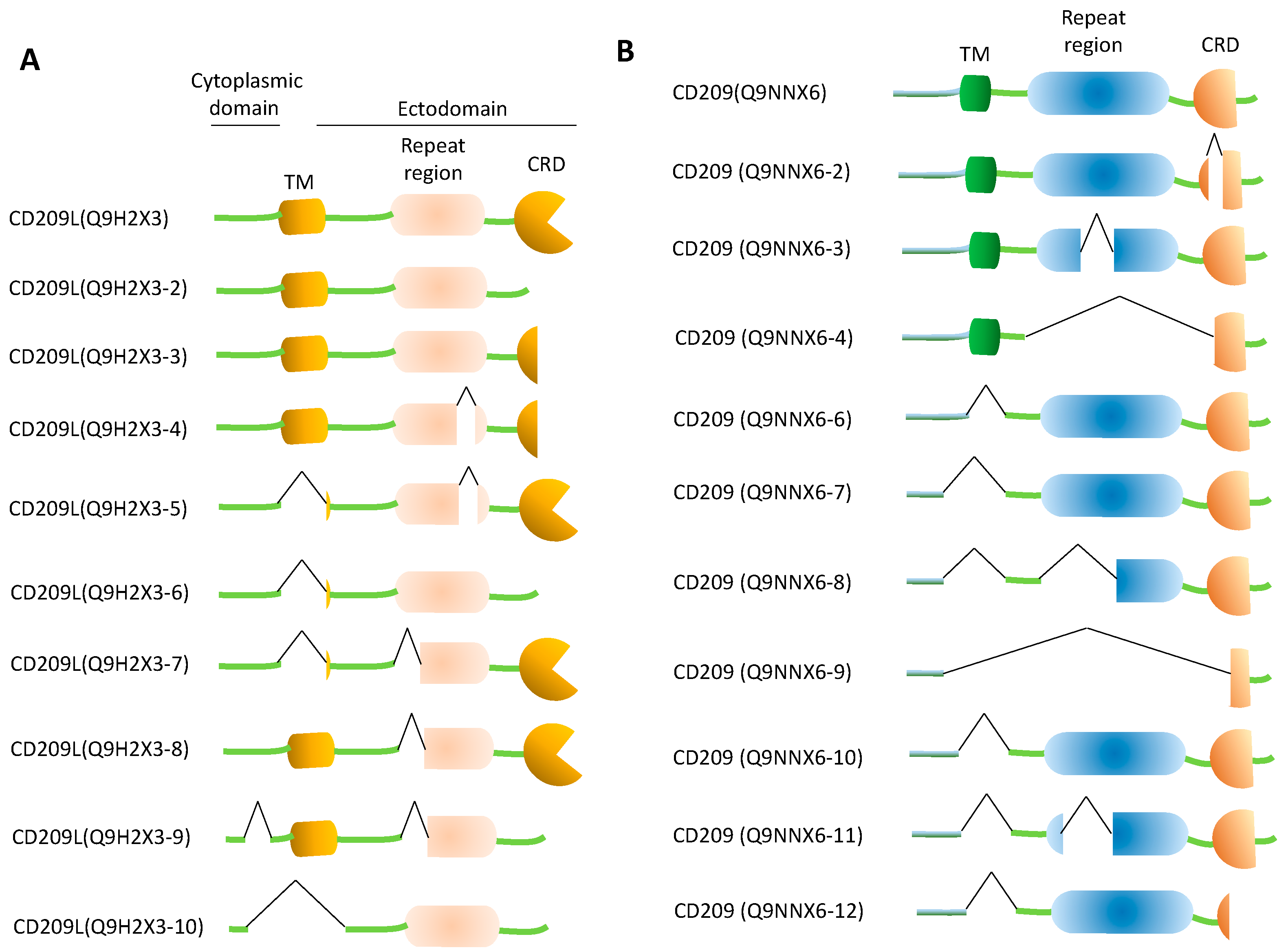
Biology, Free Full-Text
DC/L-SIGN recognition of spike glycoprotein promotes SARS-CoV-2 trans-infection and can be inhibited by a glycomimetic antagonist

PDF) CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN act as receptors for SARS-CoV-2 and are differentially expressed in lung and kidney epithelial and endothelial cells

CD209L (L-SIGN) is a receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
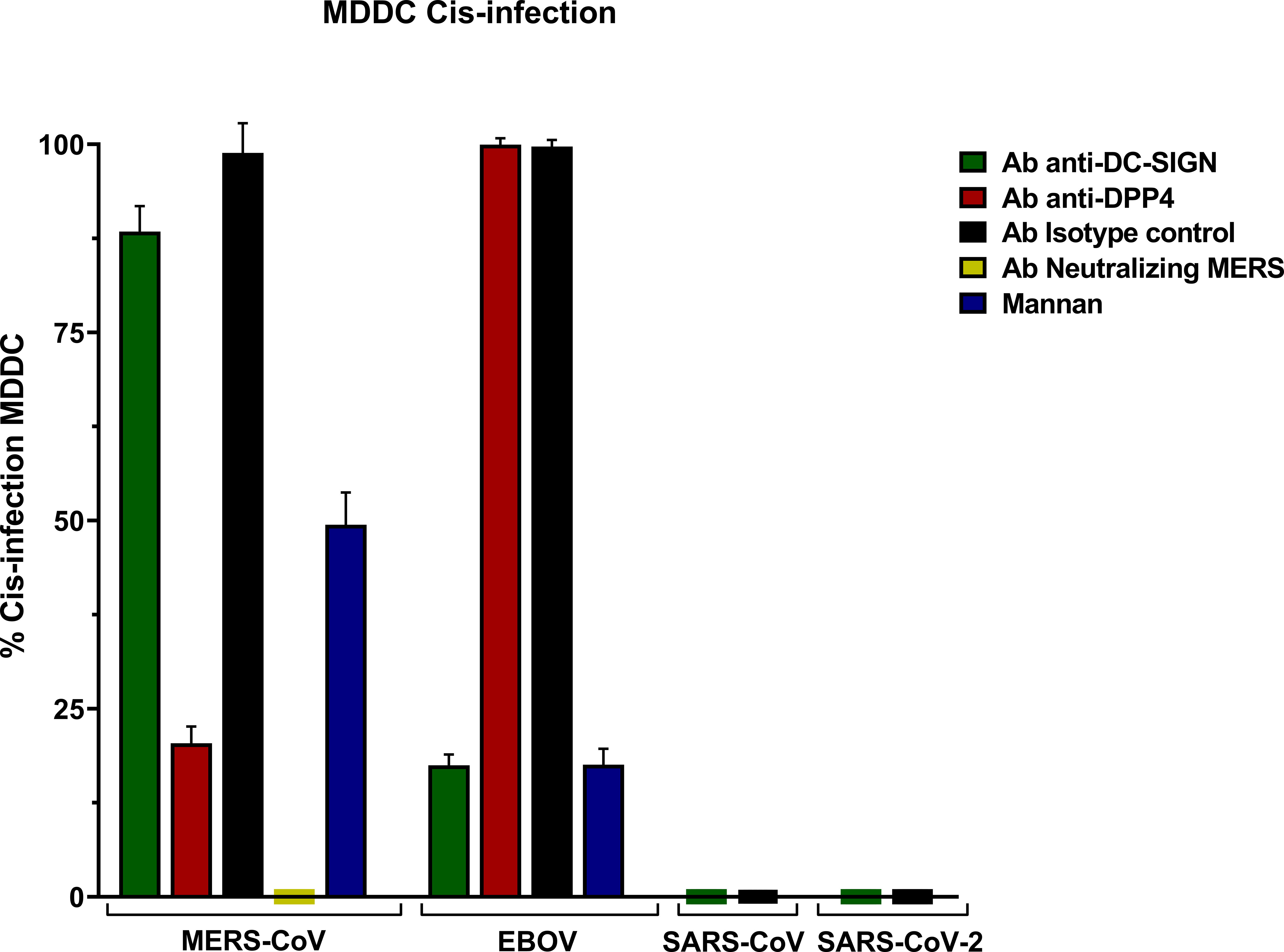
Frontiers The role of DC-SIGN as a trans-receptor in infection by MERS-CoV
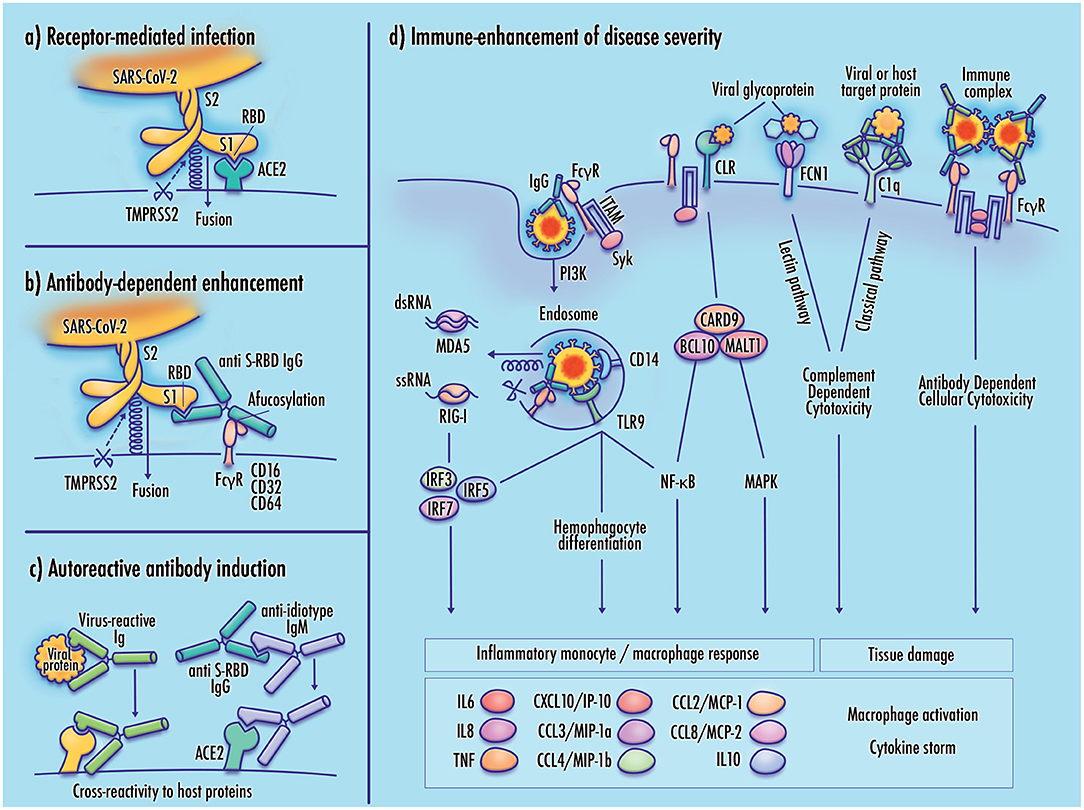
Frontiers Severe Clinical Worsening in COVID-19 and Potential Mechanisms of Immune-Enhanced Disease

From SARS and MERS to COVID-19: a brief summary and comparison of severe acute respiratory infections caused by three highly pathogenic human coronaviruses, Respiratory Research

A bird's eye view on the role of dendritic cells in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection: Perspectives for immune‐based vaccines - Galati - 2022 - Allergy - Wiley Online Library
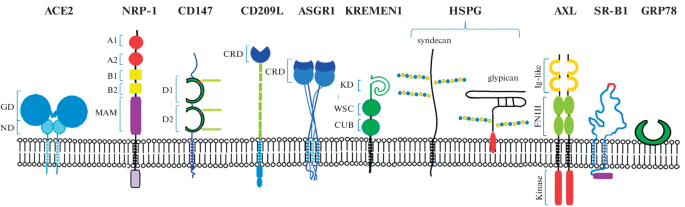
SARS-CoV-2 Receptors and Their Involvement in Cell Infection
Biology, Free Full-Text
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)