Relative Uptake, Metabolism, and β-Receptor Binding of (1R,2S)-4
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The objective of the study was to compare relative uptake, metabolism, and β-receptor affinity of the new positron-emitting uptake-1 tracer (1 R ,2 S )-4-18F-fluorometaraminol (4-FM) with those of the SPECT pharmaceutical meta-123I-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) in Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats and spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats. Methods: No-carrier-added 4-18F-FM was applied to SHR and WKY rats in vivo and to retrogradely perfused hearts in vitro. Cardiac and extracardiac distribution was assessed, and metabolite formation was determined by thin-layer chromatography. The in vivo experiments were repeated with no-carrier-added 123I-MIBG. By means of autoradiography, the β-receptor affinity of 4-FM was compared with that of MIBG and propranolol (10 μmol/L) through displacement of 125I-iodocyanopindolol (1.5 pmol/L) in slices of heart and spleen. Results: Cardiomyopathic hearts showed heterogeneous 4-18F-FM uptake with gradients up to 3.6 in vivo and in vitro between different regions of the heart. Control hearts showed such gradients in 4-18F-FM uptake only in vitro. 123I-MIBG exhibited a less heterogeneous in vivo distribution in SHR hearts. Extracardiac differences between WKY and SHR were found for uptake of 4-18F-FM in the spleen (63.3% ± 4% vs. 38.8% ± 5.7% of cardiac activity) and for renal uptake of 123I-MIBG (373% ± 27% vs. 81.4% ± 17% of cardiac activity). Metabolites of 4-18F-FM were found only in the liver and those of 123I-MIBG were found in the liver and kidney with a nearly equal relative fraction in both types of animals of about 20%, 60%, and 30%, respectively. 4-FM suppressed cardiac-specific β-receptor binding of 125I-iodocyanopindolol in heart and spleen of both types of animals significantly, whereas MIBG had almost no effect. Conclusion: The more heterogeneous cardiac distribution of 4-18F-FM suggests that it reflects alterations in uptake-1 better than 123I-MIBG in addition to the possibility of quantification and higher spatial resolution by PET compared with SPECT. Altered biotransformation in cardiomyopathic diseases may also impair the evaluation of 123I-MIBG-SPECT data. The β-receptor binding of 4-18F-FM must be further elucidated.
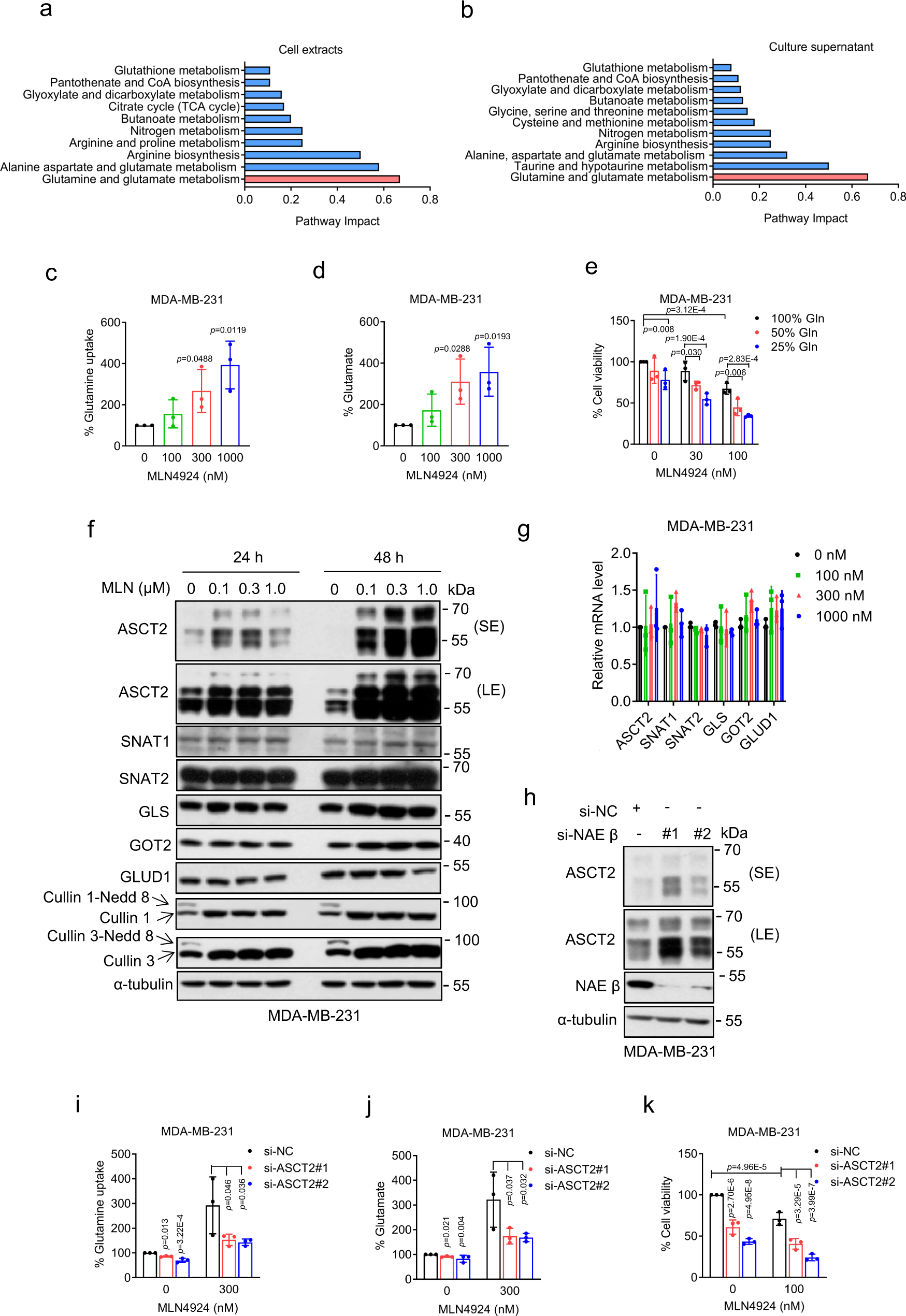
Neddylation inhibition induces glutamine uptake and metabolism by targeting CRL3SPOP E3 ligase in cancer cells

Chimeric TIM-4 receptor-modified T cells targeting phosphatidylserine mediates both cytotoxic anti-tumor responses and phagocytic uptake of tumor-associated antigen for T cell cross-presentation: Molecular Therapy

Lipoprotein(a): A Genetically Determined, Causal, and Prevalent Risk Factor for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association
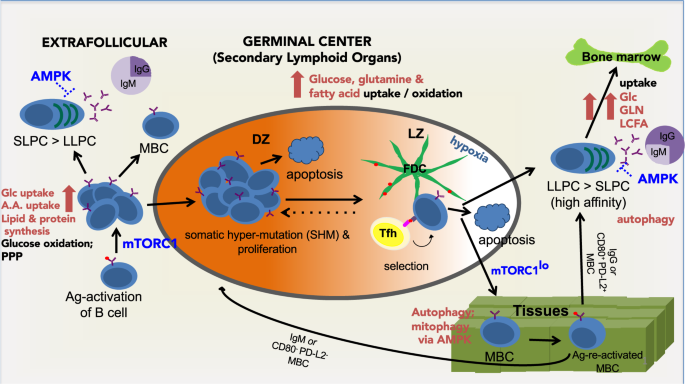
Supplying the trip to antibody production—nutrients, signaling, and the programming of cellular metabolism in the mature B lineage
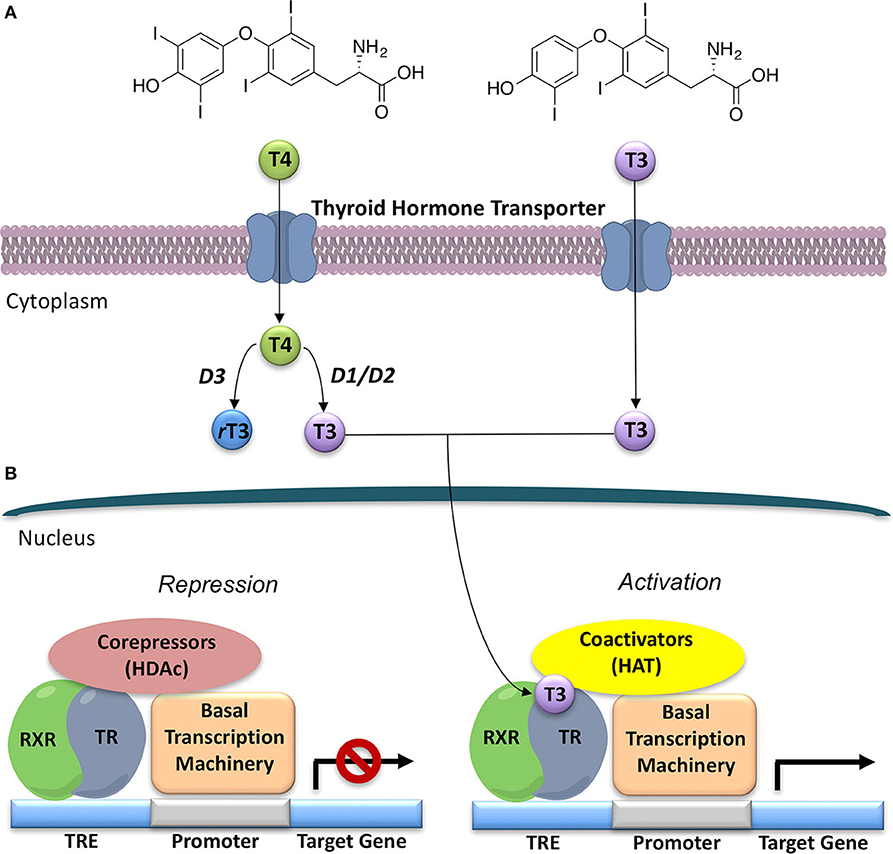
Frontiers Selective Thyroid Hormone Receptor-Beta (TRβ) Agonists: New Perspectives for the Treatment of Metabolic and Neurodegenerative Disorders

Metabolism - Wikipedia
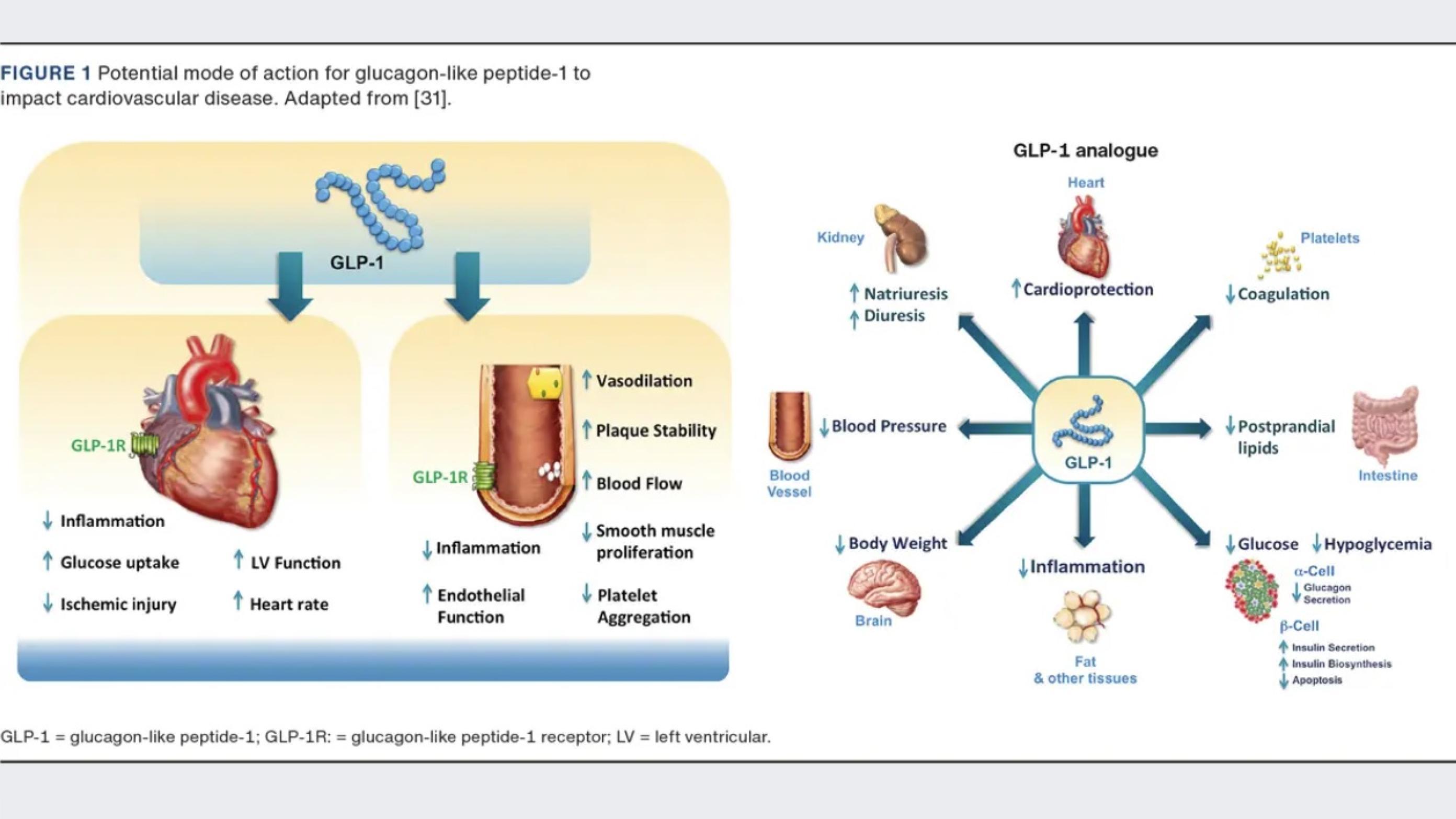
Incretin-based therapy of metabolic disease
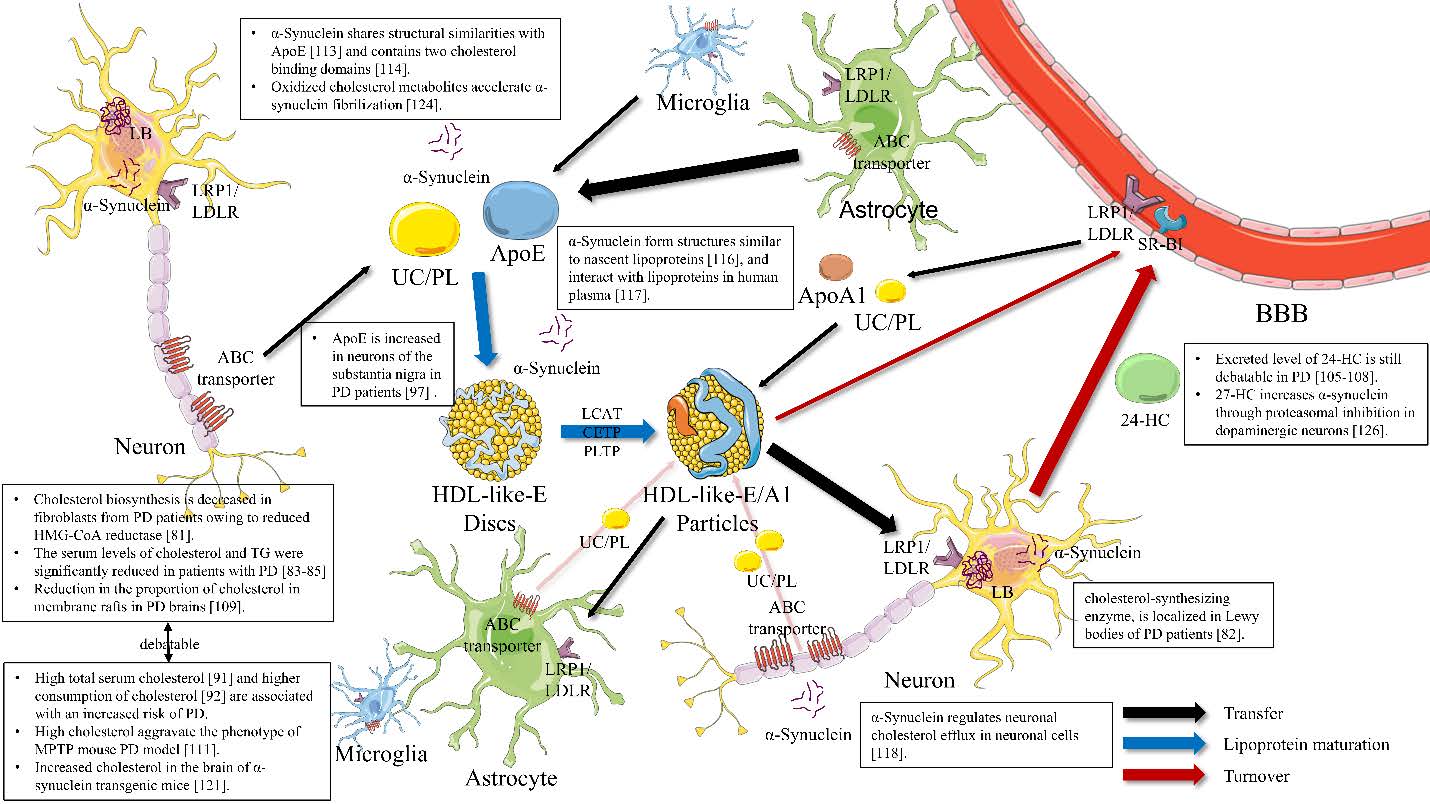
Cholesterol Metabolism in the Brain and Its Association with Parkinson's Disease
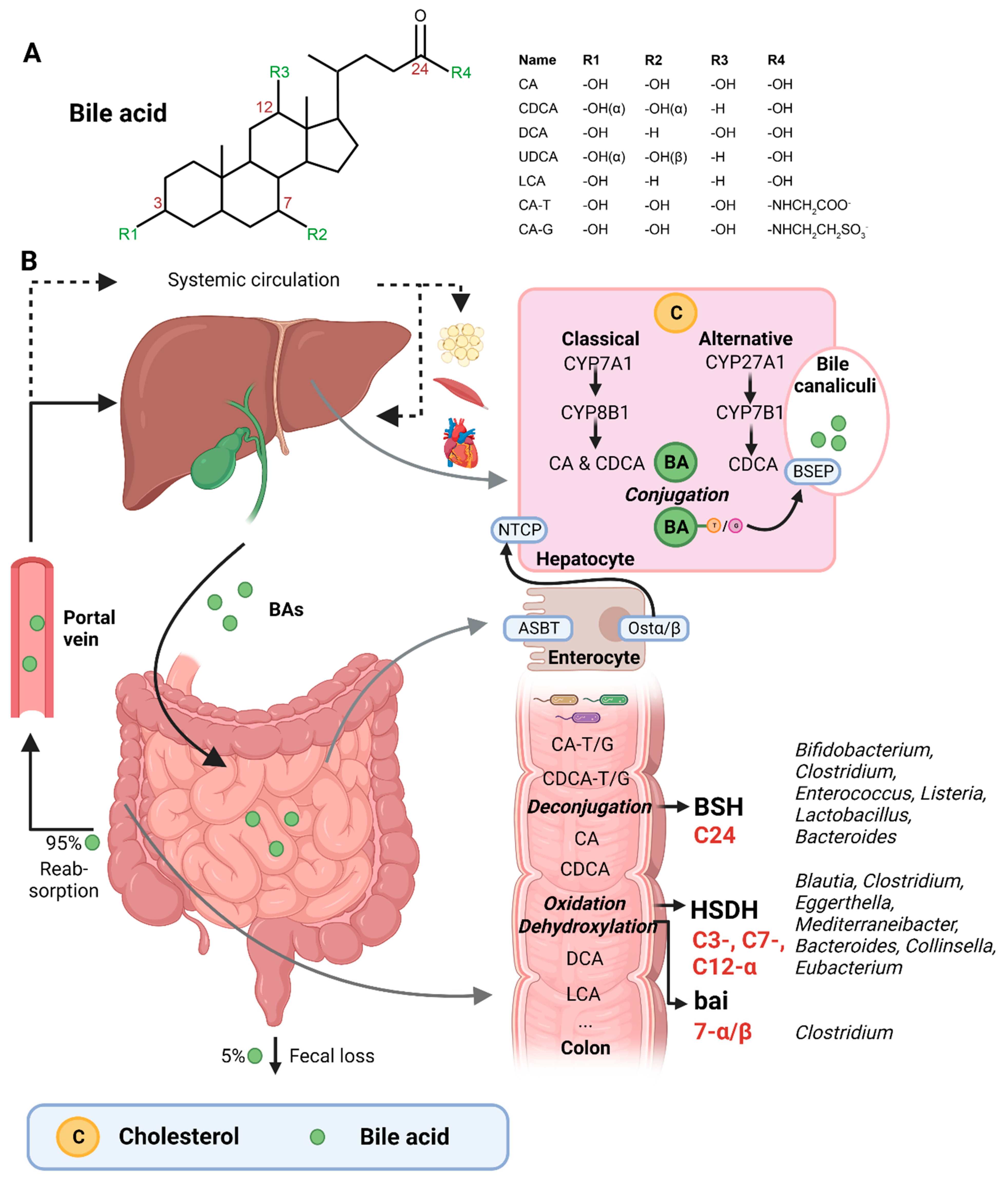
Nutrients, Free Full-Text

Lactate in the tumour microenvironment: From immune modulation to therapy - eBioMedicine
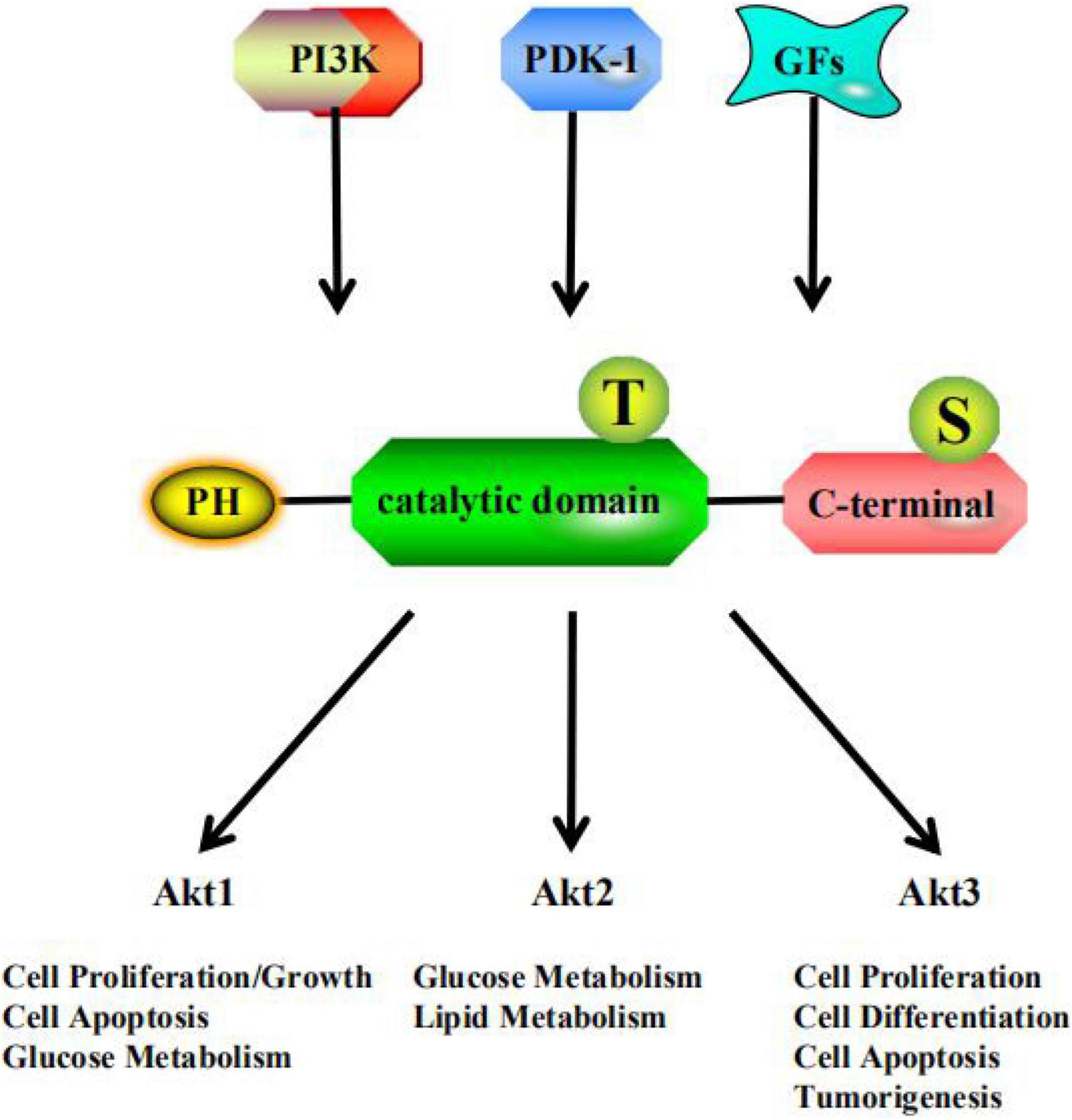
Frontiers Akt: A Potential Drug Target for Metabolic Syndrome
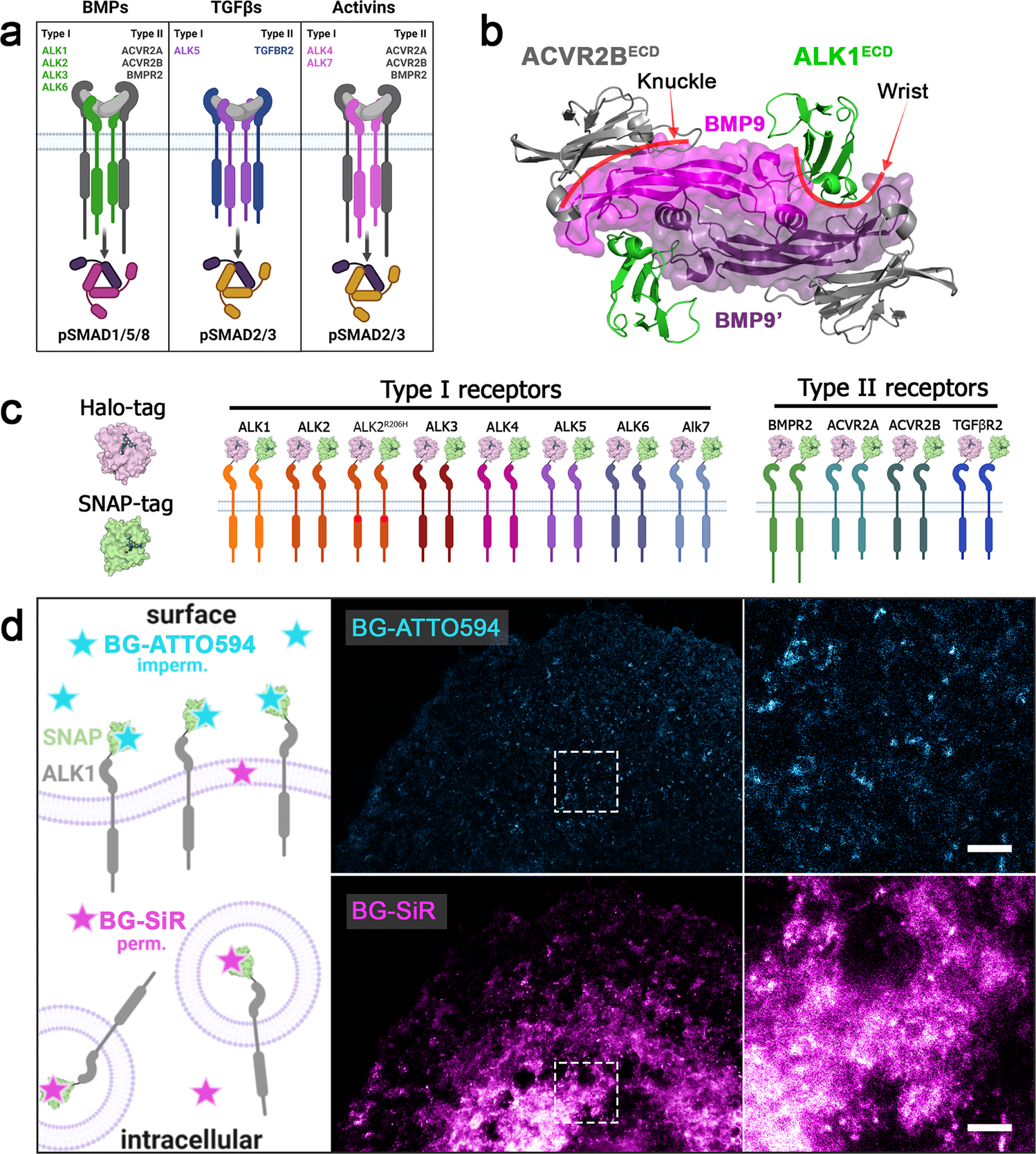
A versatile Halo- and SNAP-tagged BMP/TGFβ receptor library for quantification of cell surface ligand binding

Pathways for TRL metabolism. (A) The exogenous pathway. Dietary lipids

Insights Into Mechanisms of GDF15 and Receptor GFRAL: Therapeutic Targets: Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)