Full article: Intestinal mucin-type O-glycans: the major players in the host-bacteria-rotavirus interactions
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Intestinal epithelial glycosylation in homeostasis and gut microbiota interactions in IBD. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Human intestinal models to study interactions between intestine and microbes
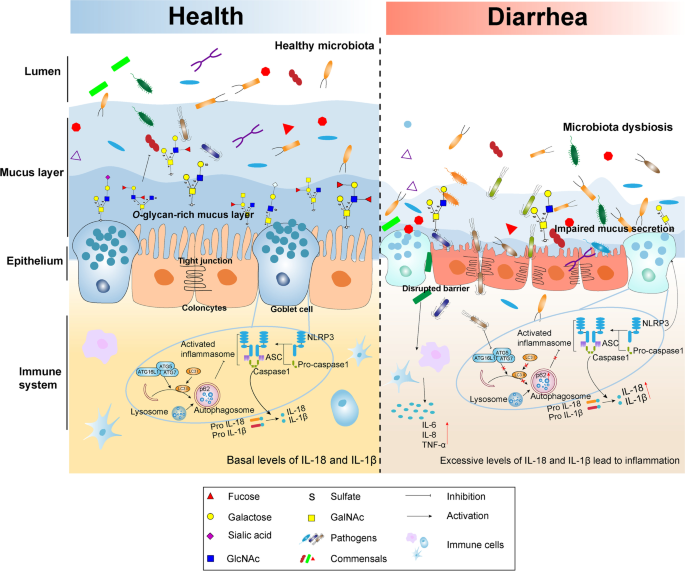
Mucin O-glycan-microbiota axis orchestrates gut homeostasis in a diarrheal pig model, Microbiome
Altered Mucus Glycosylation in Core 1 O-Glycan-Deficient Mice Affects Microbiota Composition and Intestinal Architecture
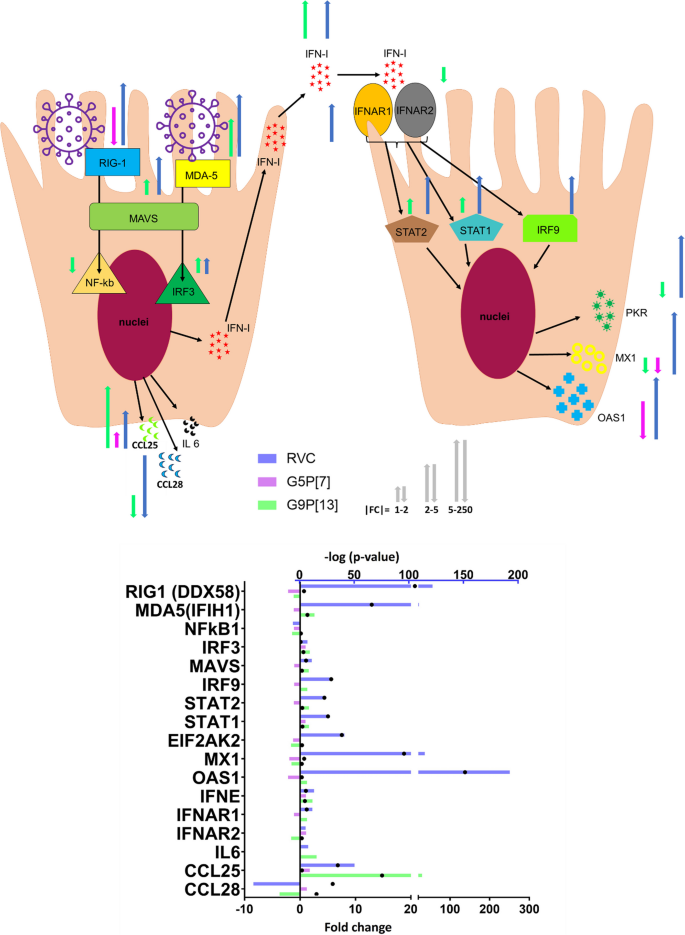
Differential transcriptome response following infection of porcine ileal enteroids with species A and C rotaviruses, Virology Journal

The Antibacterial Lectin RegIIIγ Promotes the Spatial Segregation of Microbiota and Host in the Intestine

Bifidobacterium and the intestinal mucus layer

Epithelial GPR35 protects from Citrobacter rodentium infection by preserving goblet cells and mucosal barrier integrity - Mucosal Immunology

Interactions between host and intestinal crypt-resided biofilms are controlled by epithelial fucosylation - ScienceDirect

The gut virome: A new microbiome component in health and disease - eBioMedicine
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)





